The knee joint is the largest joint in the human body. Day after day, it is subjected to enormous stresses, which in the long run can lead to signs of wear and tear. In addition, the knee is very prone to injury. So it is not surprising that many people complain about knee joint pain. Knee and spine laser center provides the wide range of the services.
Anatomy of the knee joint pain
The knee joint is a so-called hinge joint: It forms a flexible connection between the femur, the kneecap and the tibia. This is what makes it possible to bend and straighten the knee. In addition, turning movements inwards and outwards can also be carried out in the flexed state.
The anatomical structures of the knee that are prone to injury include, for example, the cruciate ligaments, the medial and medial ligaments and the meniscus.
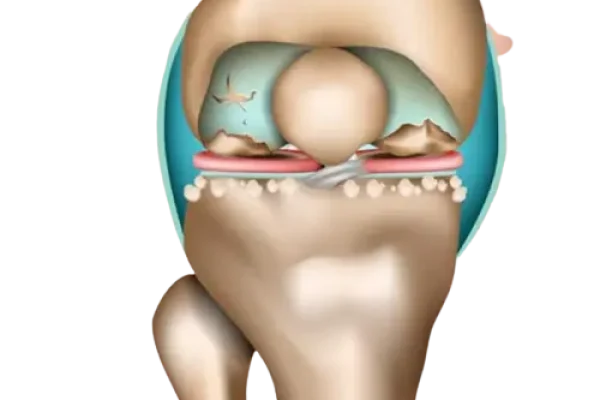
Signs of wear and tear in the knee joint are responsible for the development of knee arthrosis, which can manifest itself as pain, a feeling of stiffness and restricted movement. But wear processes can also play a role in meniscus problems.
Common knee joint pain problems
Knee pain is often due to injuries and/or wear and tear processes. Injury-related knee problems predominate in younger people, while knee pain in older people is often due to wear and tear.
Common knee problems include:
- Osteoarthritis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Cruciate ligament tear
- Meniscus damage
- Dislocation of the kneecap
- Broken bones in the area of the knee (e.g. broken tibia)
- Malpositions (e.g. knock knees, bowlegs)
Depending on the underlying cause, knee pain may have other symptoms, such as:
- swelling
- redness
- bruises
- abrasions of the skin
- mobility impairments
- Malposition or instability of the joint
Management of osteoarthritis
Even if osteoarthritis is still considered incurable, this is no reason to accept the pain and progressive cartilage loss. Effective treatment options are now available. In addition to freedom from pain, the goal is also to strengthen the articular cartilage – and thus to maintain the patient’s mobility and quality of life.
Conservative osteoarthritis therapy is based on four pillars:
- general measures
- Joint-friendly behavior in everyday life
- Gentle exercise, suitable sports
- Reduction of obesity
- Pharmacological osteoarthritis treatment
Help from the pharmacy:
NSAIDs (non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs): pain and anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. pain gel with diclofenac or ibuprofen)
Analgesics (purely analgesic effect, no anti-inflammatory component) – for example paracetamol
Cartilage-protecting substances (chondroprotective agents) such as e.g. B. glucosamine sulphate can relieve pain when taken regularly, improve mobility and strengthen the articular cartilage from the inside
Help at the doctor:
Intra-articular therapies: injection of hyaluronic acid into the affected joint
Genicular neurotomy (Radio frequency nerve ablation, Laser treatment for pain control). Latest treatment to avoid surgery.
Total knee replacement
Our Mission Is To Relieve Pain Through Simple And Easy Procedures Using Latest Technologies
– Naghmi Shirin & Dr. Shahzad Farooq
